Did you know that over 40,000 solar professionals recently gathered at the largest energy transition conference in history? This historic event highlights how decentralized energy systems are rapidly reshaping the global power landscape. Decentralized energy systems are not just a trend—they are a revolutionary movement towards empowering people and protecting the planet.
In this comprehensive guide, we dive deep into what decentralized energy systems are, why they matter, and how they are fundamentally challenging the outdated fossil fuel-based centralized power model. With insights from Jonathan Budd, CEO & Founder of Powur PBC, we explore how this movement drives resilience, independence, and sustainability.
Startling Facts About Decentralized Energy Systems and Their Growing Impact
The global momentum behind decentralized energy systems is nothing short of remarkable. Over 40,000 industry leaders and solar professionals recently convened at RE+ 2025, the world’s largest conference dedicated to solar, energy storage, and energy transition. This gathering underscored the explosive growth and widespread adoption of decentralized renewable energy technologies worldwide.
Decentralized energy systems are transforming the way energy generation, storage, and consumption occur within modern clean energy power systems. Rather than relying heavily on massive power plants controlled by a few entities, energy generation is becoming distributed across millions of homes and businesses. This shift democratizes energy access, creating a vast network of individual solar panels, home batteries, and smart energy grids.
The Rise of Decentralized Energy Systems in the Global Energy Transition
The rise of decentralized energy systems is a core driver of the global energy transition, accelerating the shift from fossil fuels to clean energy and renewable power generation. Jonathan Budd of Powur explains, “Decentralization, distributed energy… It is the future. It is the answer to resilience and independence. It’s the answer to true environmental sustainability.” This highlights how decentralized systems are integral to building an energy future that is more sustainable and equitable.
Distributed energy technologies such as solar panels and battery storage are enabling households and communities to actively participate in decentralized energy generation and consumption. This evolution supports the transition to a low-carbon economy by reducing reliance on centralized fossil fuel plants, cutting greenhouse gas emissions, and enhancing energy security at a local level.
Why Decentralized Energy Systems Matter for People and Planet
Decentralized energy systems matter profoundly because they redistribute power within the energy system — both literally and figuratively. Traditional centralized power systems have long concentrated control and wealth among a small number of stakeholders, often at the expense of people and the environment. Decentralized systems reverse this trend by empowering individuals as producers and consumers.
This democratization fosters greater energy independence, resilience against outages, and a more robust transition to renewable energy. It also addresses core social and environmental injustices perpetuated by fossil fuel extraction and centralized power monopolies. “We are the LITERAL antidote to that old model,” says Jonathan Budd, emphasizing that decentralized energy is a systemic solution aligned with human and planetary well-being.
Understanding Decentralized Energy Systems: Definitions and Core Concepts
What Are Decentralized Energy Systems? Exploring Distributed Energy and Power Systems
In simple terms, decentralized energy systems are networks of numerous small-scale energy generators and storage devices distributed across a wide area. Unlike traditional centralized power plants that generate electricity in one location, decentralized systems rely on numerous nodes — often households with solar panels and battery storage — interconnected and capable of producing, storing, and sharing energy.
This distributed energy approach improves grid resilience by reducing large-scale failures and maximizes clean energy utilization within the power system near the point of consumption. These systems are sometimes called distributed energy resources (DERs) or microgrids, reflecting their local generation and consumption nature.

Key Components of Decentralized Energy Systems: Solar Panels, Energy Storage, and Distributed Grids
The backbone of decentralized energy systems comprises three key components: solar panels, energy storage units, and distributed energy grids. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity at the source — often the rooftops of homes and businesses. Energy storage systems, such as advanced batteries, store excess electricity for use when the sun isn’t shining or demand spikes.
Distributed grids then enable seamless energy flow between these nodes, allowing households to consume, store, or even sell excess energy back to the grid or neighbors. This dynamic network creates a resilient, efficient, and clean power system daily powering millions of people.
Centralized Power vs. Decentralized Energy Systems: A Comparative Analysis
Limitations of Centralized Energy and Power Systems
Centralized energy systems rely on large-scale power plants fueled by fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas for centralized electricity generation. These plants generate vast amounts of electricity transmitted over long distances through extensive grid infrastructure. While this system has powered economies for over a century, it has significant drawbacks.
One main limitation is vulnerability: a single point of failure at a large power plant or transmission line can cause widespread outages. Furthermore, centralized systems are environmentally damaging, responsible for the bulk of carbon emissions producing climate change. They also concentrate economic and political power, often neglecting equitable access and sustainable practices.

Advantages of Decentralized Energy Systems in Renewable Energy and Energy Transition
Decentralized energy systems address many limitations of centralized energy by localizing power generation and enhancing grid resilience within the energy system. By localizing generation and storage, these systems reduce transmission losses, enhance grid stability, and accelerate adoption of renewable energy. Distributed solar panels and battery banks help communities avoid blackouts and become energy independent.
Jonathan Budd highlights that decentralized systems embody “resilience and independence,” crucial for a future less reliant on fossil fuels. This model supports a sustainable energy transition by embedding renewable energy deeply into everyday life and expanding economic benefits across broad populations rather than concentrated elites.
The Role of Distributed Energy in Building Resilient and Sustainable Power Systems
How Distributed Energy Supports Energy Independence and Environmental Sustainability
Distributed energy resources empower individuals and communities to sustainably manage their own clean energy needs within a decentralized energy power system. Solar panels combined with batteries enable households to generate clean electricity, reduce dependence on centralized grids, and lower energy bills. This creates localized energy autonomy that strengthens overall grid resilience against natural disasters or infrastructure failure.
Moreover, the shift to distributed renewables drastically cuts carbon emissions and air pollution. Integrated with smart technologies, these systems optimize energy consumption to minimize wastage and enhance efficiency, delivering important environmental and social benefits aligned with climate goals.

Expert Insights: Jonathan Budd on the Power of Decentralized Energy Systems
Jonathan Budd, CEO & Founder of Powur, explains, "Decentralization, distributed energy… It is the future. It is the answer to resilience and independence. It’s the answer to true environmental sustainability."
His reflections underscore that decentralized energy is not only a technological transition but a societal paradigm shift aimed at restoring balance in power, wealth, and environmental stewardship.
Challenges and Growth Opportunities in Decentralized Energy Systems
Building Capacity: Leadership and Entrepreneurial Growth in the Decentralized Energy Sector
Transitioning to decentralized energy systems requires visionary leadership and entrepreneurial innovation. Jonathan Budd emphasizes this growth journey as pivotal: “We are here to GROW... develop new strengths, skill sets, endurance, and capabilities.” Leaders must confront complex technical, regulatory, and market challenges to scale decentralized solutions successfully.
This process builds individual and collective capacity essential for sustaining the energy transition long term. It encourages resilience by transforming struggles into opportunities for profound personal and organizational development.

Overcoming Struggles and Misconceptions in Decentralized Energy Adoption
Despite its promise, decentralized energy systems face misconceptions, financing gaps, and technological hurdles. Some fear complexity or question reliability compared to conventional power. However, with persistent innovation and education, these obstacles diminish continuously.
Jonathan Budd reminds us that struggles are part of growth and leadership might involve “building capacity” rather than seeking easier paths. Addressing concerns openly and providing clear value to customers accelerates mainstream acceptance of decentralized energy.

Practical Applications and Examples of Decentralized Energy Systems
Real-World Examples of Decentralized Power and Renewable Energy Systems
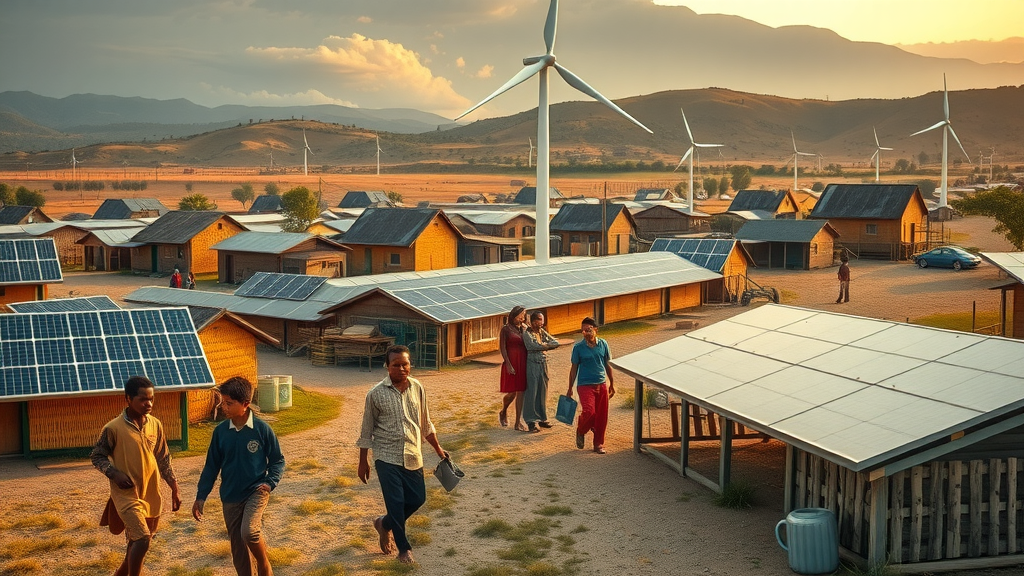
From remote villages deploying decentralized microgrids to urban neighborhoods integrating rooftop solar and battery storage, decentralized energy systems are delivering impactful clean energy solutions worldwide. These systems enable reliable electricity access in off-grid areas and foster local energy markets that spur economic development.
Such examples demonstrate not only technological feasibility but transformative social benefits, including education, health improvements, and environmental protection.

How Decentralized Energy Systems Integrate with Smart Energy and Electricity Generation
Decentralized energy systems are increasingly integrated with smart energy technologies, including IoT devices and intelligent controls, to optimize electricity generation and consumption dynamically within modern power systems. Smart home dashboards enable consumers to monitor real-time energy production, battery levels, and grid interaction, enhancing convenience and efficiency.
These innovations create a seamless user experience and support grid operators in balancing electricity supply and demand, accelerating the shift to sustainable smart electricity generation.

What You'll Learn: Key Takeaways on Decentralized Energy Systems
Definition and importance of decentralized energy systems
Comparison between centralized and decentralized power systems
Benefits of distributed energy for sustainability and resilience
Leadership growth and capacity building in the energy transition
Practical examples and future outlook of decentralized energy
People Also Ask: Common Questions About Decentralized Energy Systems
What are decentralized energy systems?
Decentralized energy systems are networks of multiple small-scale energy generators and storage units, like rooftop solar panels and home batteries, that operate locally and connect to form a resilient energy grid independent from centralized power plants.
What are decentralized smart energy systems?
These are decentralized energy systems enhanced with smart technology such as sensors, IoT, and automation that enable real-time monitoring, efficient energy management, and dynamic interaction between producers and consumers.
What are examples of decentralized power?
Examples include residential solar panels with battery storage, community microgrids, remote village solar-wind hybrid systems, and small-scale hydroelectric generators connected to localized grids.
What are the sources of decentralized energy?
Common sources are solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, small-scale hydro, biomass, and increasingly, batteries that store energy for use on demand within distributed networks.
Comparison of Centralized vs. Decentralized Energy Systems |
||
Feature |
Centralized Power Systems |
Decentralized Energy Systems |
|---|---|---|
Energy Sources |
Large fossil fuel power plants, nuclear |
Solar panels, wind turbines, batteries, small hydro |
Power Generation Methods |
Massive centralized plants feeding high-voltage grids |
Distributed small-scale generation feeding local grids |
Scalability |
Limited by central plant capacity |
Highly scalable, modular additions |
Environmental Impact |
High emissions and pollution |
Low emissions, supports renewables |
Conclusion: Embracing Decentralized Energy Systems for a Sustainable Future
Jonathan Budd of Powur reminds us, "We are part of a much larger ecosystem working to solve one of the biggest challenges on the planet. Our commitment to decentralized energy is a commitment to people, planet, and prosperity."
Take actionable steps today: explore decentralized energy solutions, engage with pioneers in the field, and develop your leadership skills to join this vital movement creating a cleaner, fairer, and more resilient energy future.
Take Action: Join the Movement Toward Decentralized Energy Systems
Explore opportunities to adopt decentralized energy solutions
Engage with communities and companies leading the energy transition
Develop leadership skills to contribute to sustainable power systems
Join Powur and Become a Leader in Decentralized Energy
Visit https://powur.com/tony.alvarez/join to start your journey
Access resources and support for decentralized energy entrepreneurs
Contribute to building a resilient and equitable energy future
Decentralized energy systems are revolutionizing power generation and consumption, providing significant benefits for individuals, communities, and environmental sustainability. To deepen your understanding of this transformative movement, consider exploring the following resources:
“Decentralized Energy Systems: Opportunities and Challenges”
This article provides a comprehensive overview of decentralized energy systems, highlighting their advantages such as increased energy resilience, reduced transmission losses, and enhanced energy access. It also discusses the economic benefits, including potential cost reductions for consumers. (ieee-energycon2020.org)
“Beyond the Grid: The Case for Decentralized Energy Systems”
This piece delves into how decentralized energy systems enhance energy security through diversification, drive sustainability by reducing carbon footprints, and empower local communities by fostering local energy production. It emphasizes the role of decentralized systems in creating a more resilient and sustainable energy future. (eiscouncil.org)
If you’re serious about understanding and implementing decentralized energy solutions, these resources will provide valuable insights into the opportunities and challenges associated with this paradigm shift.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment